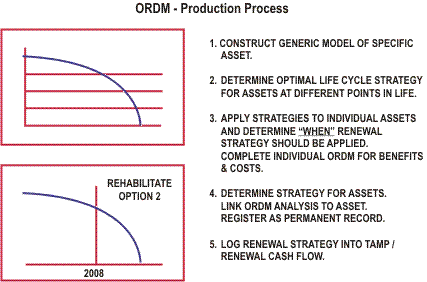
Completing an ORDM Analysis
To complete a detailed ORDM analysis a complex series of tasks is involved.
The process starts with a "generic" task list that is then expanded or retracted to suit the degree of sophistication warranted.
This generic approach is shown in the detailed task list below.
Detailed Task List
- List all assets involved in analysis
- Break individual assets down to key components with different:
- Effective life
- Consequence of failure
- Maintenance require or reliability/objectives.
- For each component/asset, identify the:
- Failure modes
- Causes of failure
- Consequences of failure
- Possible treatment options or activities to overcome or reduce failure.
- Quantify cost (economical) of the consequences of failure (risk cost).
List these as costs: - After failure
- Before failure (i.e. in a planned environment).
- Break them into key cost centers.
- Direct costs (probability of failure), including:
- Repair costs
- Damage claims (property)
- Damage claims (personal)
- Insurance excess payments.
- Indirect (ancillary) business costs (probability of failure causing these events), including:
- Environmental damage
- Loss of service/customer
- Image
- Political sensitivity
- Impact on the management system.
- Quantify costs of individual treatment options
- Identify current costs and predict future costs for:
- Maintenance
- Operations
- Loss of production.
- Identify potential benefits likely to be derived for each treatment option.
- Direct benefits, including:
- Reduced cost of repair
- Reduced operational costs
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Increased asset life — replacement deferred
- Improved productive output or income.
- Indirect (ancillary business risks) benefits, including:
- Safety (OH&S) staff and public
- Environmental
- Damage claims — property, life (personal)
- Public image
- Customer tolerance (cost of failure to customer)
- Improved level of service
- Political sensitivity.
- Complete coarse and fine filter processes, including:
- Complete filtering processes
- Complete sufficient filtering and ranking of assets with risk exposure
- Rank these
- Choose those capable of being analyzed with the available resources.
- Complete economic analysis using organizational evaluation techniques including sensitivity of assumptions (where required/or necessary).
- Identify best (apparent) strategy for asset including the:
- Lowest life cycle cost option (4% disc rate)
- Best appropriate strategy for current business environment (10% disc rate).
- Identify appropriate maintenance and condition monitoring strategy to suit recommended renewal strategy.
- Identify issues or assumptions requiring further (future) analysis, including:
- Weaknesses in this present analysis
- Areas of future potential savings — causal based, activity based, capital investment based.
- Complete full reports in accordance with organizational reporting requirements.