Advanced Asset Management – Key Principles
In assessing the ORDM strategy for individual assets it is always important to understand the part it plays in the overall life cycle asset management process.
Advanced life cycle asset management processes need to include the following functional activities:
The other key principles applicable to Advanced Asset Management are:
- Every asset needs to be considered as an individual asset. Like assets are not alike, they are only similar
- Assets don't often fail as a whole, usually only components fail and so there is a need to be able to viably rectify component failures
- The principles and concepts of asset management apply to all infrastructure assets, namely Mechanical, Electrical, Civil (passive), even to trees and grass. Only the techniques and activities are different.
A Mission Statement with respect to the organization's infrastructure assets could be:
"To plan, create, acquire, maintain, operate, rehabilitate, replace and/or dispose of the organization's infrastructure assets in the most cost effective manner whilst providing an acceptable level of service for present and future generations."
Role of ORDM in Total Asset Management Plans
Optimized Renewal Decision Making techniques can be used to assist in decisions relating to:
- Components
- Assets
- Facilities
- Systems.
The key to developing good System Plans is to ensure that we have appropriate strategies for individual assets or their components.
If we know the best answer for all components then we know the best answer for the assets. If we know the answer for all assets then we know the correct answer for the facility. If we know the answers for each facility then we know the correct plan for the asset system as a whole.
Success lies in the aggregation of component or asset strategies up to facility strategies and then system strategies.
It is only when we have the right answers for the individual components that we can develop the best life extension strategy for the asset or facility.
This is shown below:
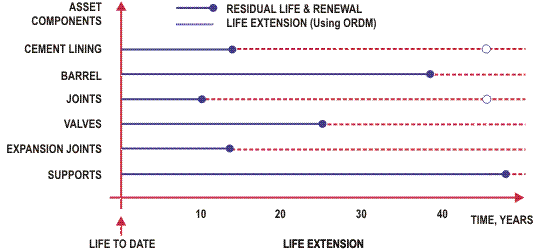
By knowing the optimal renewal treatment and the timing of that work, we can plot the optimized future cash flow for the life extension of the individual components, the sum of which represents the cash flow for the asset or facility as a whole:
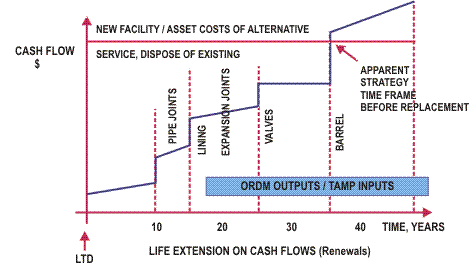
Armed with this information, we can look at appropriate strategies for the system or the organization as a whole and develop the corporate plan.
This may result in the facility being renewed (replaced) or even disposed of as part of the bigger corporate strategy.
This information can then be fed back to individual facility plans where the ORDM analysis for individual assets can be reviewed knowing that the facility need only reach a 35 year life cycle or timeframe.
The new ORDM can then be included in the current TAMP together with the renewal decision and cash flows etc.
This information "feed up" or "feed forward" and strategy "feedback" process works at all levels in an organization:
|
|
previous |
home
|
next |
|
A Future Business Perspective for Managers |
|
Repair Replace Rehabilitate Options
|
|