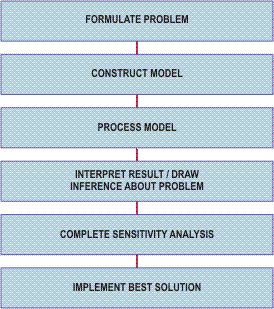
Project Evaluation
The critical issue for any project evaluation is to ensure that all treatment strategies have been considered in the first place. In many cases, an asset failure can be solved by a number of different treatment options within a single strategy, especially in the case of rehabilitation. Each option involves a different cost, time and benefit to the organization.
With increasing number of options the evaluation and decision process becomes more complex and the use of optimized decision support models is essential. The model needs to assess the:
- Increase in effective life
- Increase in level of service (if any)
- Reduction in maintenance or operations costs
- Reduction in risk cost exposure.
In general, most organizations carry out effective project evaluation assessments for major projects. However, maintenance decisions are often made without appropriate evaluation.
A decision support model could greatly assist in this area.
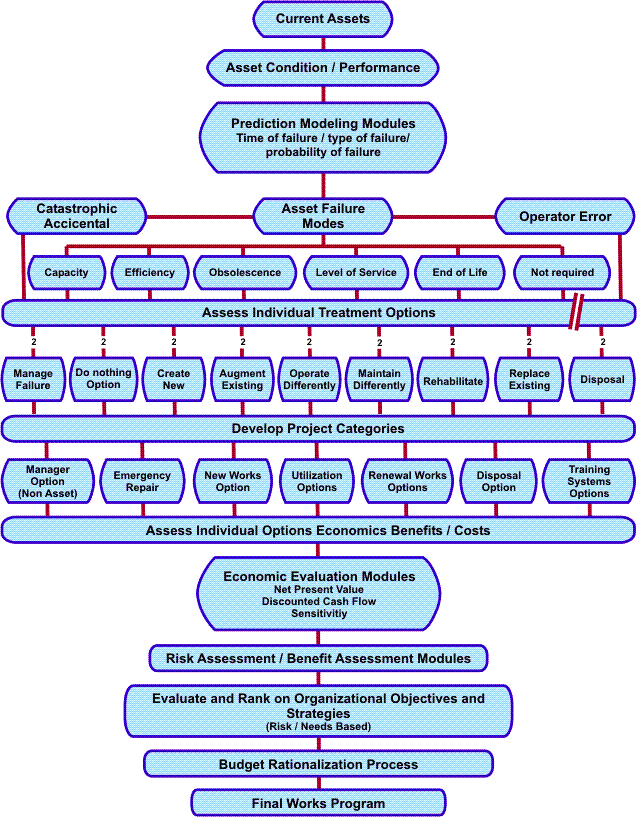
Optimized Rehabilitation/Repair decisions
For many passive reticulation assets, a predominant activity will be the reactive repair of minor asset failures. This may involve a simple repetitive activity.
In most cases, service authorities have a corrective maintenance response system that ensures these failures are corrected in a manner appropriate to their business objectives and standards.
These activities can constitute over 60% of the recurrent expenditure undertaken by an organization, and 80% of the cost of each event is involved in planning, travel, equipment provision and less than 20% relates to the actual productive work in correcting the failure. In most cases, these failures are repaired with the prime objective being the return of the asset to operational service as quickly as possible.
There is an enormous potential for service organizations to enhance their repair or renewal activity, to carry out works that will substantially reduce the overall life cycle cost of these assets by the use of a more cost effective procedures or options in treating this immediate failure.
For example, a sewer blockage is reported to the relevant authority by customers or staff. Depending on its criticality, the organization arranges for a repair crew to proceed to the site.
A good asset management system should alert this crew to the fact that this sewer has experienced several blockages in the past and will even indicate what the cause of this blockage was and its location. In this example, we are assuming that the blockage is tree roots, however other problems or causes could be similarly approached.
The problem could be solved by the simple activity of cutting and removing the obstructive roots, or a more sophisticated approach could be taken.
Armed with the historical information in relation to this sewer, its accrued costs, its impacts on the business of the authority (consequence of failure costs), and an overall economically justified renewal policy, the repair crew could:
- Assess the current failure and determine the cause of failure by the use of CCTV inspection
- Refer to the available treatment options that could be economically justified on the life cycle basis
- Choose the appropriate treatment strategy
- Carry out that treatment or arrange for specialist contractors to complete the work at an appropriate time or record this information and these decisions as the strategy for any future activities in relation to a failure of this asset
- Review the maintenance history of the asset and its recent total costs
- Complete the work and proceed to their next job.
This approach requires adequate information systems and optimized renewal decision making processes, as well as appropriately skilled staff and specialist equipment.
It is in this area that the greatest potential benefits will be derived through advanced asset management using these types of techniques. It is essential that service authorities of all types implement the necessary information systems and procedures as part of their asset management program.
In the area of infrastructure asset management, decisions have to be made as to whether the asset has to be maintained, renewed, or replaced at different stages during the life of an asset. If the asset is still in brand new condition the decision may be "Do Nothing".
The most logical process for responsible asset management is to identify the assets that are critical to the organization and to consider the various options available to replace or rehabilitate these assets so that the required level of service and performance is achieved.
Replacement will bring back full performance, whereas some renewal options may not quite restore to full performance, but will provide a level of service suitable to ratepayers or customers, and within the standards set by the organization. Rehabilitation techniques using different treatments may derive different benefits for the assets concerned and the users.
Asset Managers need to be able to assess the relative merits of the various options and optimize these through a decision making process by considering:
- The capital required for each option
- When that capital investment will be required
- The effective life of the different treatment options e.g. the time before further investment will be required
- An assessment of the benefits that will be derived from each treatment options.
The relative differences between these various investments can then be evaluated. A net present value assessment, together with adequate sensitivity analysis, is a suitable procedure. However, matching this with an assessment of the different benefits, the various levels of service, the options offered is a more complex matter, particularly given the long effective lives of the various options.
For each treatment strategy, there are usually different options. For example, in the maintenance of road pavement, the treatment options may involve bitumen reseals of varying thickness.
In the current business environment of reducing budget, many capital and recurrent expenditures have to be reviewed. Works have to be prioritized and these can only be achieved effectively through a rational decision making process.