An Example of the ORDM Process
One problem faced by many authorities is the prediction of failures as compared with the actual failures that may occur.
As assets age and their condition deteriorates, the number of failures varies significantly due to many variables such as:
- Original construction quality
- Variable decay rates
- Material weaknesses and rate of decay
- Environmental factors
- Operational factors
- External loadings and stresses.
In general the numbers of failures will vary significantly from year to year and as such we often find it difficult to determine the accurate long-term trends for these failures.
This is shown below:
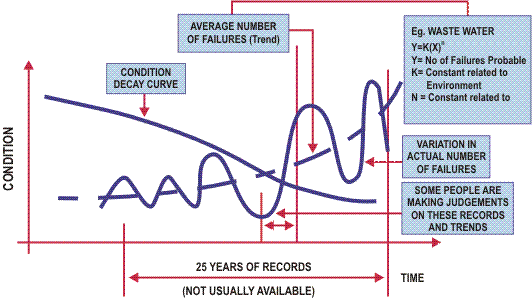
The overall trends of failures, disregarding those failures that are not associated with the age of the asset equates to the formula shown in the following diagram.
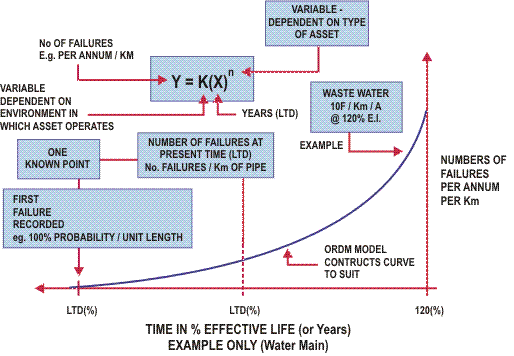
The basis of typical approach to this study has been:
- To assess the condition of the asset, looking at the various distress failure modes and to score these modes in such a way as to allow the rating of condition of individual sections of the asset
- To relate these condition scores to the performance of the asset and to determine approximate effective lives for the parent assets
- To develop decay curves that can relate the predicted condition to a predicted performance
- To assess the cost of this predicted performance.
Using this data we are then able to predict the future costs likely to be incurred, as shown below:
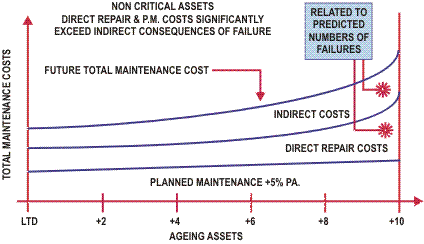
Different treatment options are then assessed against this predicted cost and the potential savings are recognized.
By completing a cash flow of the various options the most cost effective option can be identified as shown in the following figure.
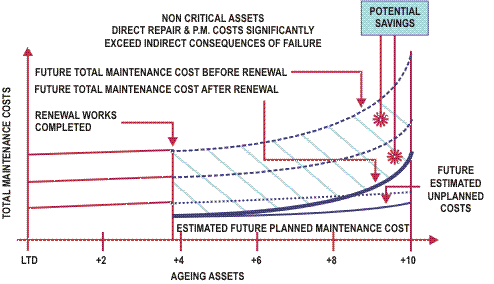
The potential savings for each option will vary with time and it is desirable to identify the most cost effective point for the renewal to be completed:
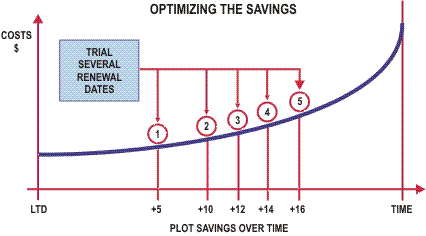
By completing this type of analysis we can then identify the point at which the greatest potential savings or highest NPV is likely to occur and determine that as the point for which renewals should take place.
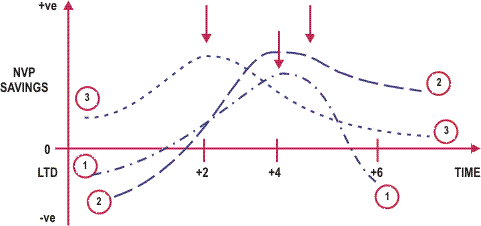
This detailed analysis requires significant inputs through both the number of sensitivity assessments and the various timing of the options.